DESIGN.
BUILD.
TEST.
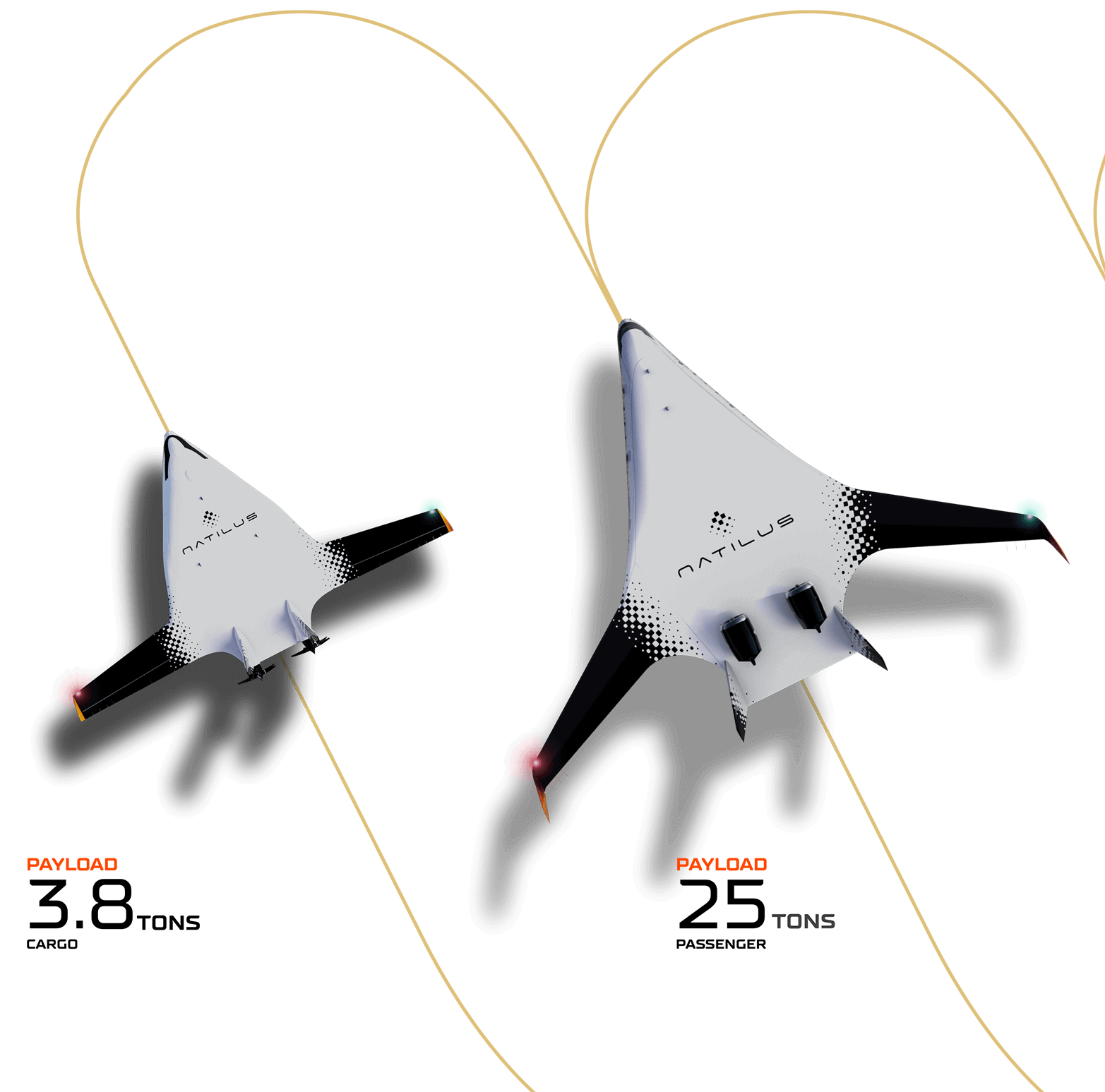
With improved fuel efficiency and the room to accommodate future propulsion technologies, BWB aircraft can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, addressing environmental concerns in aviation.